Smart Manufacturing: Everything You Need To Know
Manufacturing has undergone a digital transformation. The traditional factory floor has evolved into an interconnected, data-driven environment known as smart manufacturing – an approach that aims to improve manufacturing and production processes.
Smart manufacturing adoption grew by 50% last year,1 and it's not hard to see why. Organizations that implement manufacturing IT solutions can optimize their operations, maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and much more.
If you haven't embraced smart manufacturing yet, it's time to get on board. In this blog, we'll explain what smart manufacturing is, how it helps manufacturers solve challenges, and how you can start leveraging it today to modernize your business.
What Challenges Do Midwest Manufacturing Companies Face?
Optimizing your operations to reduce downtime, improve your bottom line, and support the supply chain requires taking a proactive approach to your IT – which isn't always easy to come by in the Midwest.
Manufacturing businesses in Milwaukee and Chicagoland often struggle to:
- Gain more flexibility and efficiency by moving workflows to the cloud.
- Protect your network from advanced cyber security threats.
- Streamline your systems for fewer communication breakdowns.
- Plan for incidents that could cause disruptions and lost productivity.
Adopting smart manufacturing technologies can help you overcome these challenges and keep your operations running smoothly.
What Is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is the use of advanced technologies to create an automated manufacturing process. It leverages Internet of Things sensors, big data analytics, artificial intelligence, robotics, and machine learning to monitor and control manufacturing systems in real-time.
With smart manufacturing, businesses can increase efficiency, improve product quality, save money, and more. It signifies a transformative shift from traditional manufacturing processes towards a more digitized and networked production model.
Some characteristics of smart manufacturing include:
Connectivity
In a smart factory, all devices, systems, and machines are networked together and can communicate critical data via sensors. This connectivity allows for increased visibility across operations.
Automation
Advanced robotics and AI take over dangerous, repetitive, and routine manufacturing tasks, freeing up the human workforce for higher-value work and improving safety.
Data Analytics
Smart manufacturing solutions collect, aggregate, analyze, and turn the vast amounts of operational data created during operations into real-time insights that drive decision-making.
Adaptability
Thanks to the abundance of data and flexibility of smart manufacturing machines, production lines can quickly adapt to accommodate changing customer demands and market trends.
Predictive Capabilities
By combining data patterns with machine learning, smart manufacturing solutions enable manufacturers to predict potential equipment failures, quality issues, output gaps, and more before they occur.
The History of Smart Manufacturing
The original Industrial Revolution began around the mid 1700s, and manufacturing systems have gotten faster, stronger, and more efficient ever since.
While the First Industrial Revolution was defined by steam power, the Second Industrial Revolution introduced the assembly line and mass production processes. Data-enhanced automation was developed during the Third Industrial Revolution, and the latest iteration – the Fourth Industrial Revolution – is where we are today.
The term "smart manufacturing" came into widespread use when GE coined the phrase "Industrial Internet" to describe adding sensors, software, and big data processing capabilities to manufacturing operations. Over the next few years, developments in industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), AI, and cloud computing drove further advances in internet-connected machinery and the smart manufacturing ecosystem.

What Related Technologies Enable the Smart Manufacturing Process?
Smart manufacturing leverages advanced technologies to create an efficient, interconnected production system. Some of the key technologies enabling the smart manufacturing process are:
Industrial Internet of Things
IIoT devices are at the heart of digital manufacturing. They include industrial devices and sensors used to collect data from internet-connected machinery, which helps improve manufacturing performance, reduce downtime, and more.
Artificial Intelligence
As manufacturing data grows, more organizations are turning to artificial intelligence to supplement human analysis. Around 74% of manufacturers currently use or plan to use AI,1 which can analyze generated data to uncover inefficiencies, predict issues, and make data-driven decisions.
Digital Twin Modeling
Digital twins are virtual representations of products or systems. Manufacturers use digital twins to simulate the production process in a virtual environment, allowing them to test and optimize processes before implementing them in the real world.
Automation and Advanced Robotics
Advanced robots powered by AI and sophisticated sensing technologies can take over repetitive and labor-intensive tasks with precision and consistency. These machines function alongside operators to improve worker safety and reduce human error.
Predictive Analytics
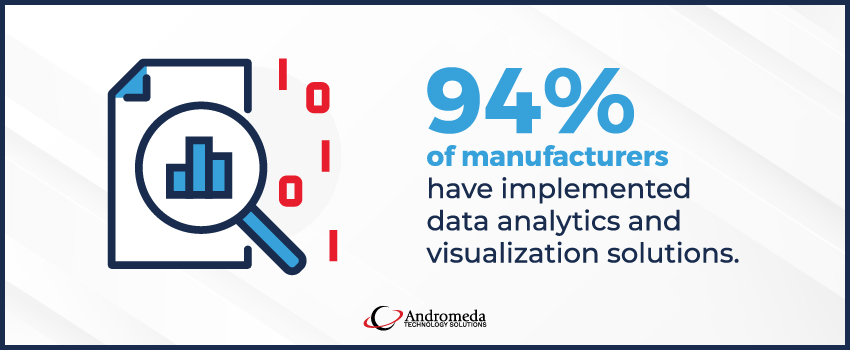
94% of manufacturers use data analytics and visualization to streamline the supply network.2 Predictive analytics take a technology-driven approach to drawing insights from manufacturing data through predictive modeling, machine learning, and digital twin modeling.
Cloud and Edge Computing
Cloud platforms offer centralized access to manufacturing data across multiple locations – while also providing the immense computing power needed for big data analytics. Edge computing brings processing power closer to data sources, reducing latency and delivering real-time decision-making at the production site.
Additive Manufacturing
Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing enables cost-effective, on-demand production of highly customizable final parts and products. It reduces waste and the need for spare part inventories.
Cyber Security
Cyber attacks targeting manufacturing companies accounted for nearly 25% of the total attacks in 2022.3 With so much interconnected technology at stake, cyber security solutions like network encryption, access controls, malware protection, and multi-factor authentication are essential for securing your data network.
Blockchain
Smart factories that provide supply chain management are exploring blockchain technology for its transparency, traceability, and security as a fast and efficient way to record and store manufacturing data.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Augmented and virtual reality can provide immersive, flexible technical workforce training simulations while assisting human workers on the factory floor through hands-free instructions and information.
Pros and Cons of Smart Manufacturing
Like any transformative technology, smart manufacturing comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Read on to explore the pros and cons of the smart manufacturing movement.
Smart Manufacturing Pros
- Increased Efficiency - Smart manufacturing technologies streamline operations, eliminating wasteful processes and enhancing overall productivity. Real-time data helps identify bottlenecks, allowing for swift corrective measures.
- Quality Control - With automated quality assurance checks and data analytics, smart manufacturing covers manufacturing inadequacies by reducing errors and ensuring consistent product quality.
- More Flexibility - With the ability to rapidly adjust programmed instructions and access real-time data, smart manufacturing facilities can seamlessly shift between product variants and volumes to align with consumer demand.
- Reduced Environmental Impact - By optimizing resources and reducing waste, smart manufacturing initiatives can positively impact your sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Lower Costs - Operational efficiencies, waste reduction, better asset utilization, and optimized energy usage lower overall manufacturing costs.
- Improved Safety - Connected worker wearables, collaborative robots, and virtual and augmented reality simulations enhance safety by reducing direct human contact with hazardous equipment.
- Better Decision Making - By leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and analytics, smart manufacturing equips business leaders with the insights needed for more informed strategic decisions.
Smart Manufacturing Cons
- High Upfront Investment - Transitioning to a smart factory typically requires hefty capital investments in sensors, connectivity, automation equipment, analytics software, and technical skills.
- Increased Complexity - Integrating advanced technologies into the production process can add significant complexity, requiring skilled professionals to manage and maintain your systems.
- Potential Cyber Security Risks - With increased connectivity comes an increased risk of cyber attacks. Strong cyber security measures are integral to protecting your critical data.
- Organizational Resistance - Adopting smart manufacturing requires changes in legacy systems, processes, and mindsets that some employees may resist.
- Dependence on Technology - A heavy reliance on digital information technology can cause significant disruption if your systems fail or experience technical issues. Regular maintenance and updates can help mitigate these risks.
How Is Smart Manufacturing Different From Traditional Approaches?
Smart manufacturing has gained momentum over the past few years, but how exactly does it differ from its conventional counterpart? Here are some of the biggest differences between smart manufacturing and traditional manufacturing processes:
Automation
Where traditional manufacturing is heavily dependent on human labor, smart manufacturing takes a technology-driven approach to production by leveraging automation tools like robotics, IoT, and artificial intelligence.
Supply Chain
Traditional supply chains were linear, with limited visibility and coordination. Smart factories are integrated across departments and partners for transparency and responsiveness across the supply chain.
Data Usage
In traditional production processes, collected data was minimal and siloed. Smart manufacturing applies sensors and internet-connected systems across the factory to collect and analyze data for real-time insights.
Adaptability
Traditional systems relied on manual adjustments to adapt to changes, which was slow and inefficient. Smart factory systems use real-time data and industrial connectivity devices to automatically adapt production.
Decision-Making
Decisions in conventional manufacturing were made by managers in a centralized, top-down approach. Smart manufacturing enables decentralized, localized decision-making using analytics at an edge device level.
Customization
Traditional systems relied on assembly lines with limited flexibility. Smart manufacturing uses a modular design for rapid prototyping, which makes it easy to produce customized or small-batch products.
Interoperability
In traditional factories, communication between different manufacturing machines can be limited or nonexistent. Smart manufacturing thrives on connectivity, enabling seamless data sharing, coordination, and communication between various parts of the production process.
Workforce Skills and Training
Traditional manufacturing relies on a skilled workforce, but employees often lack specialization in areas like data analytics and digital technology. With smart manufacturing, teams must be able to operate, maintain, and troubleshoot systems effectively, which may require upskilling and training programs.
Maintenance
In traditional manufacturing, maintenance was routine-based. Smart manufacturing uses predictive maintenance analytics to assess equipment performance and predict maintenance needs ahead of time.
Modernize Your Manufacturing Processes With Andromeda
Smart manufacturing can transform your production into an intelligent, interconnected ecosystem – but selecting the right technologies is key to getting the most value for your efforts.
Andromeda has helped businesses in the manufacturing industry implement best-fit technology solutions for over 27 years. We know having the wrong technology in place or relying on outdated systems can leave manufacturers in the Midwest struggling to stay competitive, which is why we take a proactive – not reactive – approach to modernizing your operations.
Ready to start your smart manufacturing journey? Book a meeting with our network infrastructure experts today.
Sources:
Keep Your Business Safe, Secure, and Running
We’ll take a proactive approach to your manufacturing IT – and help your business blast off.





